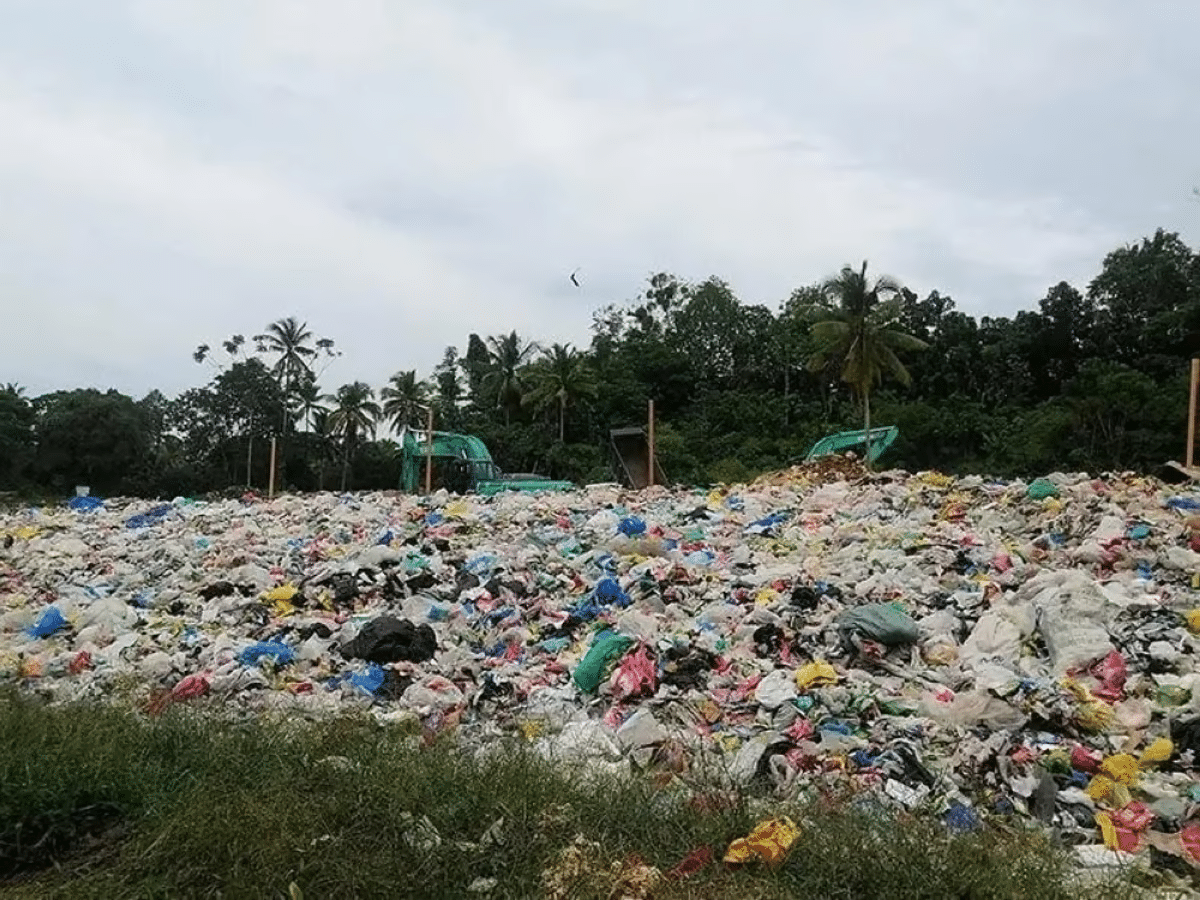
Waste disposal is a serious environmental issue. To help deal with this, the Philippine government has recently adopted waste-to-energy measures, with the hopes of addressing the country’s sustainable energy needs as well. In fact, Davao has been considering the use of waste-to-energy technology in order to solve their landfill issues.
What Is Waste-To-Energy?
Waste-to-Energy (WTE) is the method by which waste is converted to heat or electricity. This could be done by either incinerating garbage or breaking it down to produce biogas or synthetic gas.
It offers a possible solution to countries with waste disposal challenges as well as an urgent need for sustainable energy. But there is an ongoing debate surrounding this new technology. Let’s look at the pros and cons of using waste-to-energy technology.
PROs of Waste-To-Energy
1. Sustainable Waste Disposal Method
By using garbage as an energy source, you’re already putting waste to good use. Instead of allotting large swaths of real estate for waste, you can eliminate it while generating energy in the process.
Many cities today are struggling with waste management issues, as landfills are having a hard time accommodating increasing waste volume. Davao’s waste output, for instance, has already increased by 700 to 800 tons this year. An effective waste-to-energy facility could be a big help to the city’s landfill problems.
2. Converts Garbage To Clean Energy
When harnessed effectively, waste can be converted to heat or electricity. In a sense, it’s a way to recycle waste into something we actually need, which is energy generated from sources other than fossil fuels.
Power sourced from fossil fuels leads to more carbon emissions, which hastens climate change. If we find more alternative sources of energy, then we can help lessen our carbon footprint. Waste-to-energy technology is “clean” energy in more ways than one: it helps eliminate waste from our lands while providing a greener energy source.
3. Complements Recycling Efforts
Waste segregation is an important aspect of recycling. Through the incineration stage of the waste-to-energy process, some stronger materials like metal can survive. This means that the WTE process has a built-in waste segregation feature. By eliminating every other kind of unusable waste, you can recover other materials that can still be reused, repurposed, or recycled.
CONs of Waste-To-Energy
1. Potentially Harmful Emissions
WTE methods that rely on waste incineration can emit pollutants in the air. These include carbon, dioxins, furans, particulate matter, and heavy metals. If not regulated properly, a waste-to-energy facility can be harmful to the environment.
2. Technology Is Expensive
Waste-to-technology is relatively new technology and is usually expensive. Building a WTE plant involves high costs and so do maintenance and operation costs.
3. Relatively Less Energy Efficient
Compared to other renewable forms of power generation, waste-to-technology is not as efficient. Generally, total energy efficiency can be up to 25% using WTE methods. In comparison, many of the newer solar panels produced in recent years have an energy efficiency of up to 50%.
Some critics of waste-to-energy methods point to this fact, saying that its potentially harmful effects far outweigh the benefits and the energy it’s able to generate.
Hope For The Future?
Waste-to-energy technology is still evolving, with improvements still being made in order to lessen or eliminate the pollution it’s causing. The newest WTE facilities that are being built across the globe have advanced pollution control and odor control features that help ensure the health and safety of the people living nearby.
Responsible WTE implementation involves adherence to strict emission standards. It also includes proper identification and treatment of hazardous components and making sure that none of its residues are released into the atmosphere.
If our country is to embrace this new technology, then it’s important that we adopt the newest and best practices in the world so that we can truly tap into its “clean energy” potential. When done right, waste-to-technology could be an ideal solution to two of our most rampant problems: waste disposal and sustainable energy.