The environment is in crisis and the country is pivoting to supplementing and eventually replacing fossil fuels with renewable energy. But how is renewable energy actually beneficial for the environment?
Climate change: The driving force
The reason the shift to renewable energy is urgent and critical is because of climate change.
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) defines climate change as “a long-term change in the average weather patterns that have come to define Earth’s local, regional and global climates.”
While natural factors can influence the climate, human activities, particularly through the emission of greenhouse gasses, have accelerated climate change at an alarming rate.
The environmental impact of climate change
The effects of climate change are far-reaching and devastating. Human-caused climate change has led to the loss of sea ice, shifting seasons, and melting glaciers. Sea levels are rising, threatening coastal communities. Extreme weather events such as hurricanes, heat waves, wildfires, droughts, floods, and heavier-than-normal rainfall are becoming more frequent causing loss of lives and livelihoods. For example, at the beginning of 2024, rains caused floods and landslides across Mindanao island, affecting more than 1.7 million people.
The root of the problem: Greenhouse gas emissions
Increased greenhouse gas emissions (GHG) are at the root of climate change. GHG–primarily carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide emitted through the burning of fossil fuels for energy–accumulate and form a blanket around the earth, trapping heat. Normally, GHG emissions would dissipate into space and pose no harm. But, because human activity is emitting greenhouse gasses at monstrous levels every day, the gasses linger in the atmosphere, suffocating the planet.
Increasing populations and electricity needs have led to the installation of more power plants emitting more harmful GHG emissions. If we continue to burn fossil fuels for energy, the planet’s surface temperature will keep heating up causing more extreme weather conditions and making our world unlivable. To lessen GHG emissions, we need to switch to cleaner sources of energy.
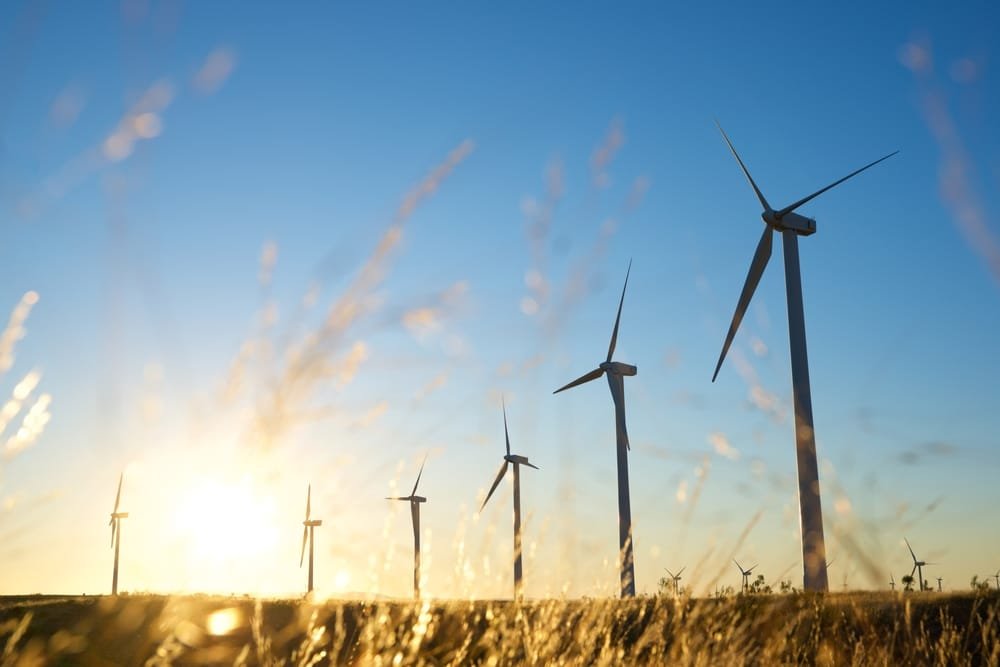
Renewable energy: A cleaner alternative
Renewable energy is a cleaner source of energy since it emits little to zero pollutants and GHG emissions. Renewable energy sources are solar, wind, hydro, biomass, and geothermal energy. Unlike fossil fuels, renewable energy is abundant, available, and naturally replenishing.
Environmental benefits of renewable energy
Renewable energy is better for the environment because it causes little to no harm compared to fossil fuels. Its environmental benefits are:
- Low to Zero GHG emissions.
- Reduced air and water pollution. Renewable energy does not release pollutants, unlike fossil fuels.
- Minimal damage to land and oceans. Fossil fuel extraction damages animal habitats, oceans, and forests. On the other hand, renewable energy does not leave long-term effects on land and seas.
- Conservation of water resources. Converting renewable energy to electricity does not require large amounts of water unlike fossil fuel power plants that need water for cooling.
Sustainability
Renewable energy is sustainable, meaning that it can meet people’s current needs while ensuring that future generations can also meet their energy requirements.
Continuous research and technological advancements are also making renewable energy more accessible and affordable. In fact, the International Energy Agency has reported that at present, solar energy is the cheapest energy available.
Renewable energy plays a vital role in mitigating climate change and nurturing the environment.
It is also paving a clear path for humankind towards a sustainable future.
References:
What Is Climate Change? | Facts – Climate Change: Vital Signs of the Planet (nasa.gov)
Renewable energy, facts and information (nationalgeographic.com)
Renewable energy – powering a safer future | United Nations
Renewable Energy Explained (nationalgeographic.org)
Renewable energy and its importance for tackling climate change | Natural History Museum (nhm.ac.uk)
20240216_ACAPS_Briefing_note_Philipines_floods_and_landslides_in_Mindanao_Island.pdf